Knowledge-Infused Prompting: Assessing and Advancing Clinical Text Data Generation with Large Language Models
 The overview of CLINGEN.
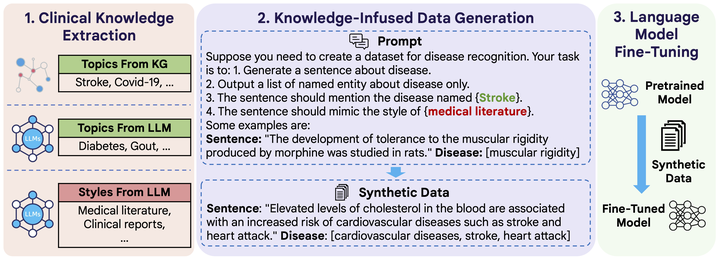
The overview of CLINGEN.Clinical natural language processing requires methods that can address domainspecific challenges, such as complex medical terminology and clinical contexts. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have shown promise in this domain. Yet, their direct deployment can lead to privacy issues and are constrained by resources. To address this challenge, we delve into synthetic clinical text generation using LLMs for clinical NLP tasks. We propose an innovative, resourceefficient approach, CLINGEN, which infuses knowledge into the process. Our model involves clinical knowledge extraction and context-informed LLM prompting. Both clinical topics and writing styles are drawn from external domainspecific knowledge graphs and LLMs to guide data generation. Our extensive empirical study across 7 clinical NLP tasks and 16 datasets reveals that CLINGEN consistently enhances performance across various tasks, effectively aligning the distribution of real datasets and significantly enriching the diversity of generated training instances. We will publish our code and all the generated data in https://github.com/ritaranx/ClinGen.